
The primary functions of the ballast bed are providing a uniform transmission of the traffic load from the rail to the subsoil and enabling a high resistance of the sleepers to longitudinal and lateral displacement. Moreover, it guarantees the elasticity of the track to reduce the dynamic stresses and enables easy restoration of the track geometry by tamping. The ballast bed performs its tasks best if it is compacted continuously and optimally.
Dynamic track stabilisation is primarily used in connection with tamping.
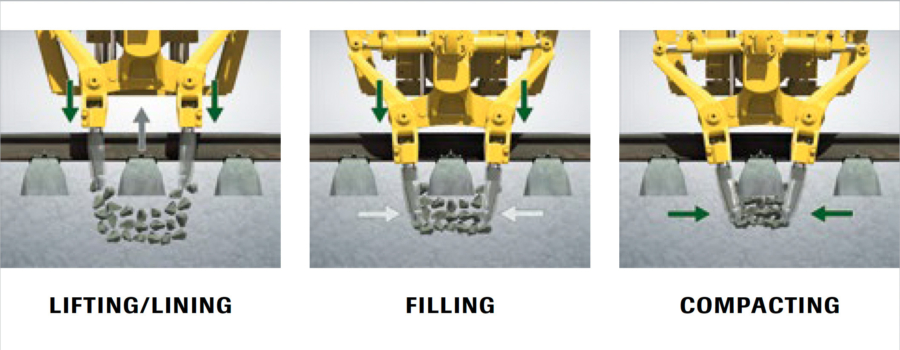
Tamping is a method that produces the correct track geometry. Clamps place the track in the desired position by lifting (vertical) and lining (horizontal) it. Then, vibrating tamping tines push together and compact the ballast below the sleepers to maintain the corrected track geometry.
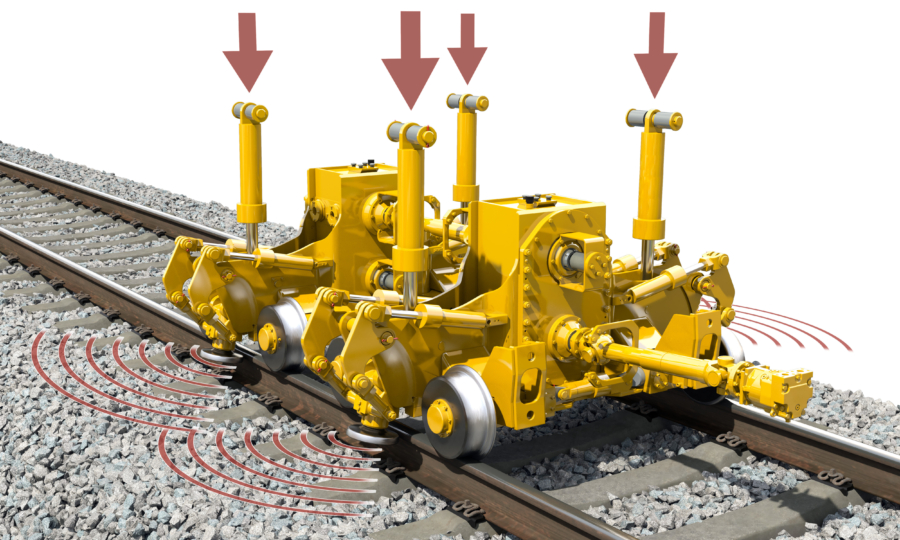
In other compaction methods used in track maintenance, vibrating stamps are pressed on the free ballast surface. In contrast, dynamic track stabilisation introduces dynamic excitation into the ballast via the track panel. This excitation is realised as horizontal, or, to be exact, lateral vibrations. At the same time, a static vertical load is applied. The result is a spatially homogeneous compacted ballast bed and an increased track geometry stability.